

Environmental Health
Business Overview
SIIC's environmental health business covers various sectors, including highways, water services, solid waste power generation, photovoltaic power generation, and offshore wind energy.
-
Core Enterprises
SIIC Environment Holdings Ltd.
SIIC Environment Holdings Ltd. ("SIIC Environment") is a leading integrated company in China's water and environmental protection sector, boasting a registered capital of CNY5.29 billion. The company is headquartered in Singapore and is listed on the Singapore Exchange's main board, having successfully joined the Hong Kong Stock Exchange main board in 2018. Its primary operations include wastewater treatment, water supply, sludge treatment, solid waste-to-energy incineration, and other related environmental services.
SIIC Environment is an active investor and operator in the environmental protection industry, with over fifteen years of operating history in China. It currently has six divisions: Wuhan Branch, South Water, Shandong Branch, Longjiang Environmental Protection Group, Fudan Water, and Ranhill Utilities, as well as controlling the shares and operating of Baojingang Company. As of the end of 2023, SIIC Environment manages approximately 250 wastewater treatment and water supply projects across China, with a total capacity of 13.16 million tons per day; 5 solid waste-to-energy incineration projects with a capacity of 6,550 tons per day; and 13 sludge treatment projects with a capacity of 3,155 tons per day. Its operations extend across 20 provinces, municipalities, and special administrative regions nationwide.
SIIC Environment, with its unique strategic positioning and business model, will continue to expand its water services and solid waste management operations while actively seeking market opportunities in other environmental sectors. These include industrial wastewater treatment, seawater desalination, sludge treatment and disposal, soil remediation, renewable energy, water treatment technologies, and pollution prevention. The company is committed to continually increasing its market share, enhancing its scale and efficiency, and consolidating its leading position within China's top list of the water and environmental protection industry.
——Representative Projects (Selected)
Shanghai Baoshan Renewable Energy Utilization Center: This project went into operation in September 2022 and has been active for two years. It can manage 3,000 tons of dry waste and 800 tons of wet waste per day, generating roughly 800 million kilowatt-hours of renewable energy each year and decreasing carbon dioxide emissions by 330,000 tons. This facility is the first of its kind in Shanghai to offer integrated end-of-life waste disposal for both dry and wet waste following the city's implementation of waste sorting, effectively tackling waste disposal issues in its service area and improving the harmlessness and resource utilization rates of waste. In line with the guiding principles of "leading technology, advanced processes, near-zero emissions, and neighborly operations," this project aims to set a new standard in China's renewable energy sector.
Xicen Water Purification Plant: Located within the Yangtze River Delta Integrated Demonstration Zone, this plant is designed to process 50,000 tons of water per day. It serves as a key facility supporting Huawei Qingpu R&D Center and Xicen S&T Innovation Center. The plant began operation on June 30, 2024, and is currently undergoing process testing. The facility will be built entirely underground, complying with the Class III surface water discharge standards, making it among the best in the country. Above ground, the area is planned to be a water culture landmark, enhanced with landscaping, lighting, and other aesthetic designs. This project aims to be a high-quality representation of ecological and green integrated development in the Yangtze River Delta.
-
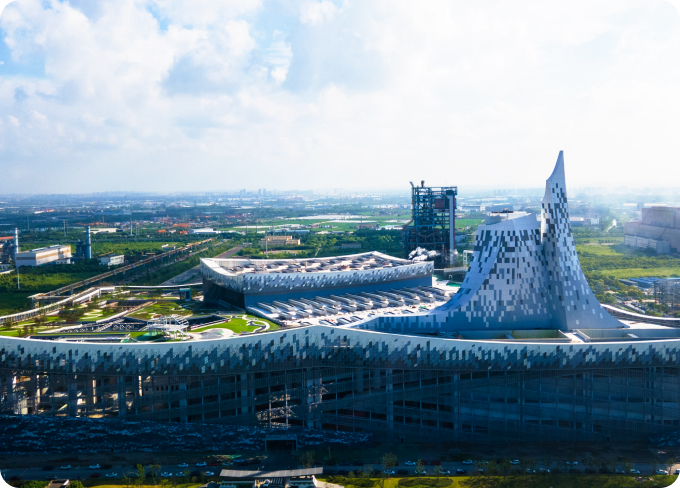
 Shanghai Baoshan Renewable Energy Utilization Center
Shanghai Baoshan Renewable Energy Utilization Center -
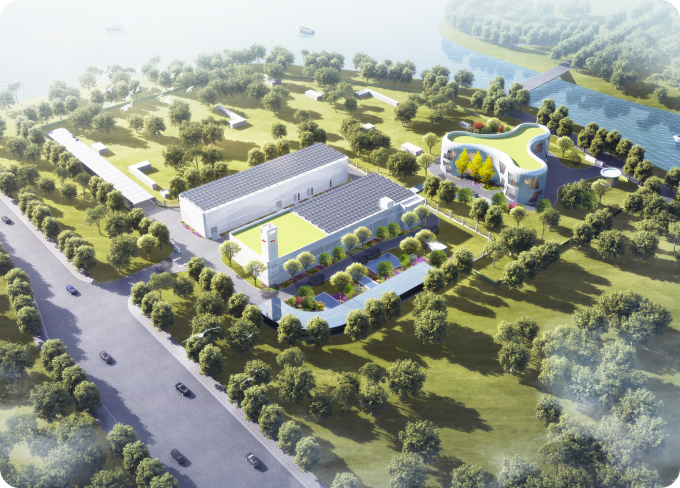
 Xicen Water Purification Plant
Xicen Water Purification Plant -
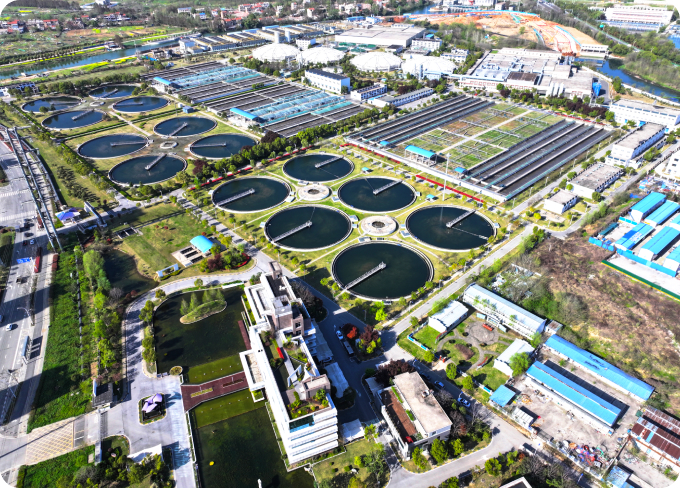
 Yinchuan Fifth wastewater treatment Plant
Yinchuan Fifth wastewater treatment Plant -
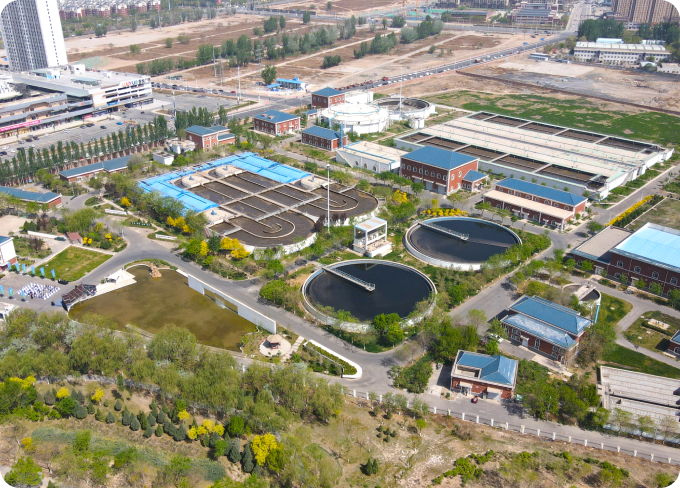
 Wuhan Hanxi Wastewater Treatment Plant
Wuhan Hanxi Wastewater Treatment Plant -
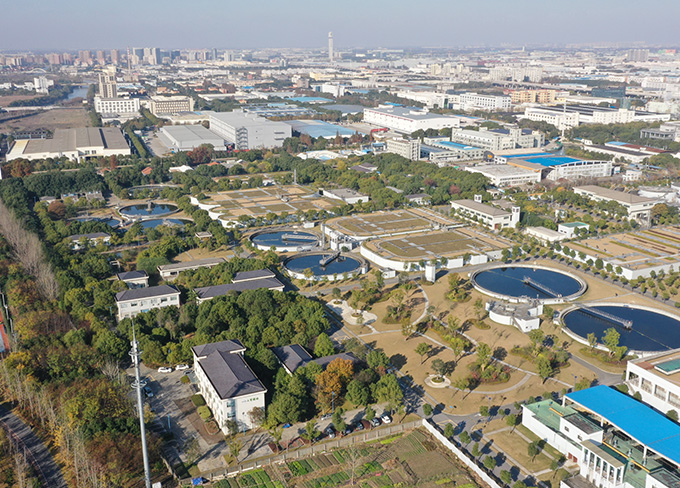
 Shanghai Qingpu Second Wastewater Treatment Plant
Shanghai Qingpu Second Wastewater Treatment Plant -
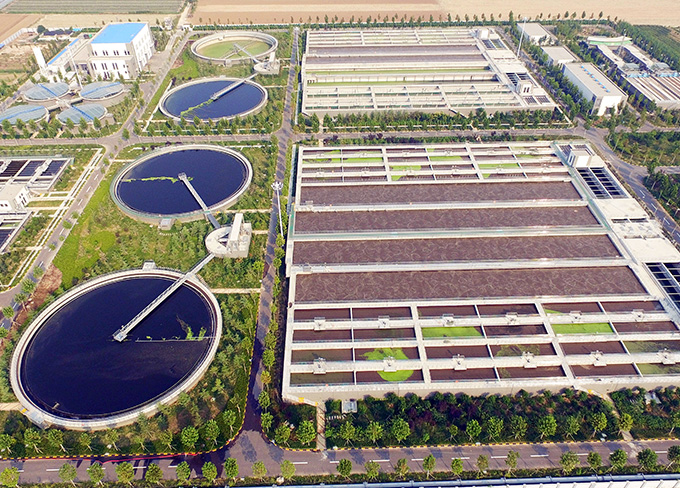
 Weifang City Wastewater Treatment Plant
Weifang City Wastewater Treatment Plant -
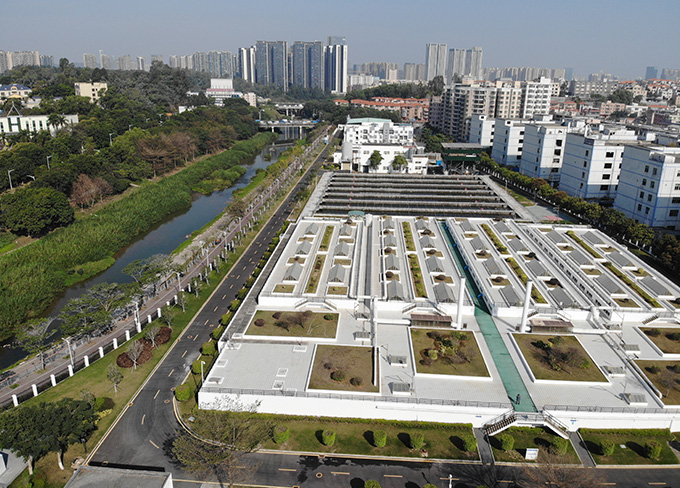
 Henggang Wastewater Treatment Plant
Henggang Wastewater Treatment Plant -

 Cixi City Hangzhoubay New Distract Water Purification Plant
Cixi City Hangzhoubay New Distract Water Purification Plant -

 Shanghai Fengxian West Wastewater Treatment Plant
Shanghai Fengxian West Wastewater Treatment Plant -
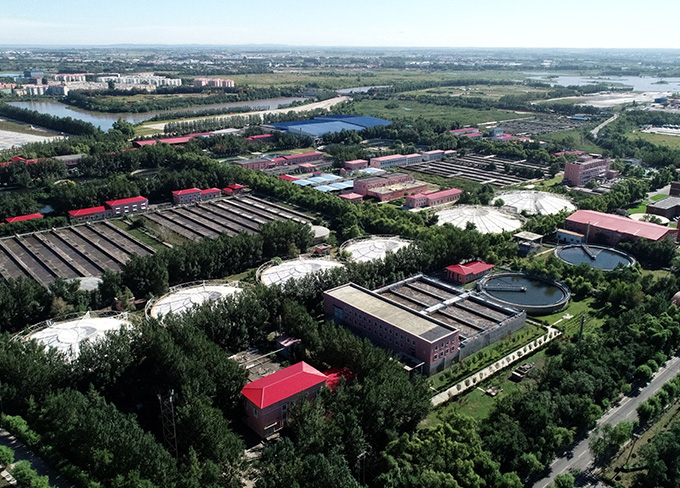
 Harbin Taiping Wastewater Treatment Plant
Harbin Taiping Wastewater Treatment Plant -
 Mudanjiang Wastewater Treatment Plant
Mudanjiang Wastewater Treatment Plant
-
-
Shanghai Cyber Galaxy Investment Co.,Ltd
Founded in November 1999, Shanghai Cyber Galaxy Investment Co.,Ltd is a specialized investment and asset management platform focusing on clean energy, under the umbrella of SIIC. As of the end of June 2024, Xinghe Digital owns and manages a total of 15 large-scale grid-connected solar photovoltaic power plants, spread across nine provinces and municipalities, with a total capacity of 740 MW. Additionally, the company is actively involved in domestic wind power investments.
-
 Gansu JiaYuGuan TaiKe 100MW Photovoltaic Power Station
Gansu JiaYuGuan TaiKe 100MW Photovoltaic Power Station -
 Inner Mongolia Hohhot Shenzhou 30MW Photovoltaic Power Station
Inner Mongolia Hohhot Shenzhou 30MW Photovoltaic Power Station -
 Ningxia Zhongwei Taike 30MW Photovoltaic Power Station
Ningxia Zhongwei Taike 30MW Photovoltaic Power Station -
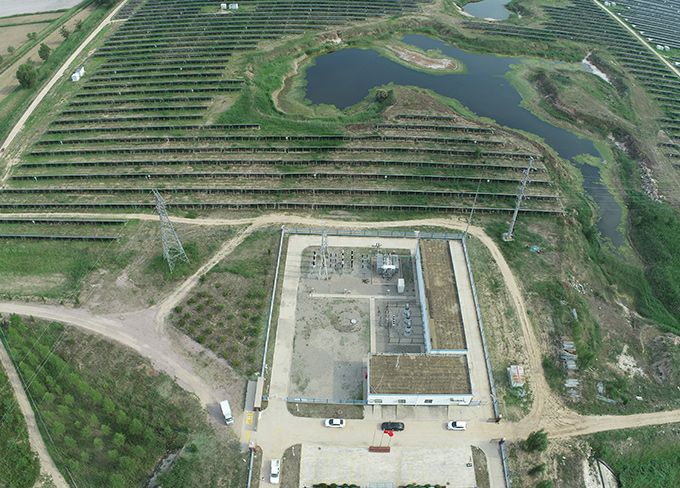
 Shanxi Xinzhou Hengneng 50MW Photovoltaic Power Station
Shanxi Xinzhou Hengneng 50MW Photovoltaic Power Station -
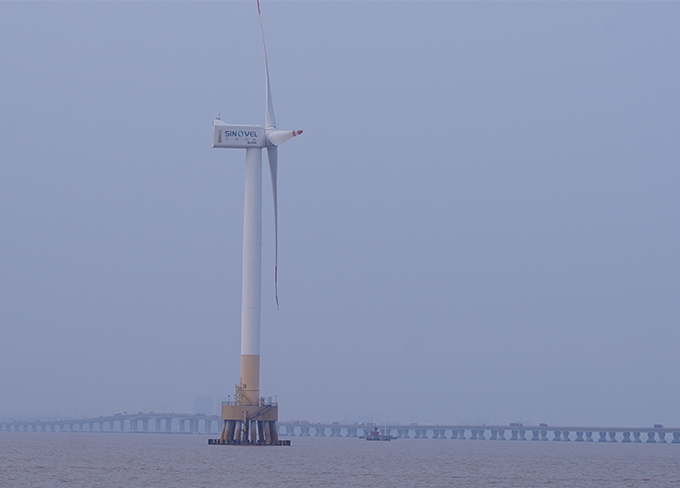
 Donghai Wind Power Station
Donghai Wind Power Station -
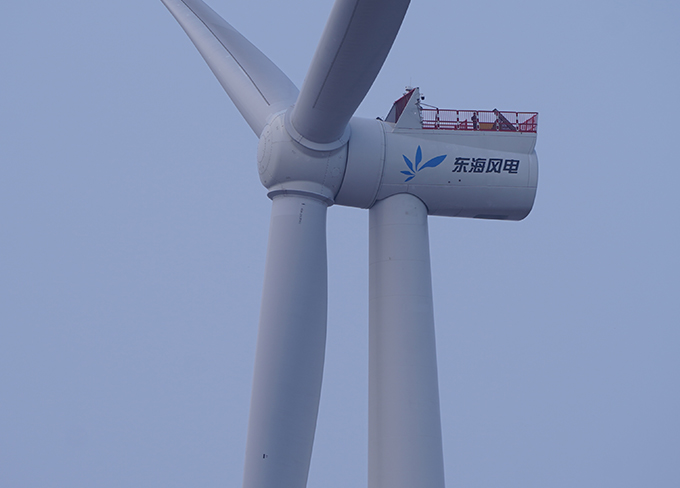
 Donghai Wind Power Station
Donghai Wind Power Station -
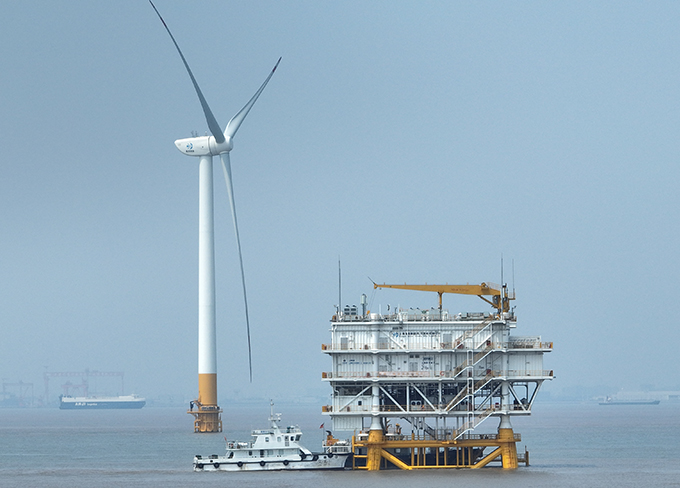
 Fengxian Offshore Wind Power Station
Fengxian Offshore Wind Power Station -
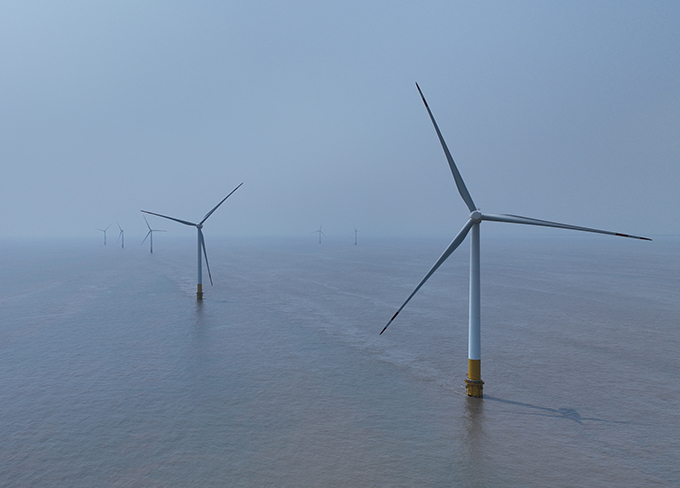
 Fengxian Offshore Wind Power Station
Fengxian Offshore Wind Power Station
-
-
G2 Jing-Hu Expressway (Shanghai Section)
The G2 Jing-Hu Expressway (Shanghai Section) spans 26.04 kilometers, starting from Zhenru in Putuo District and extending west to connect with the Jiangsu section at Huaqiao in Kunshan, Jiangsu. This expressway mainly traverses Putuo, Jiading, Minhang, and Qingpu districts, serving as a major transportation artery linking Shanghai with other provinces and cities. It is also part of the expressway that connects Shanghai to Chengdu (G42 Shanghai-Chengdu Expressway).
-
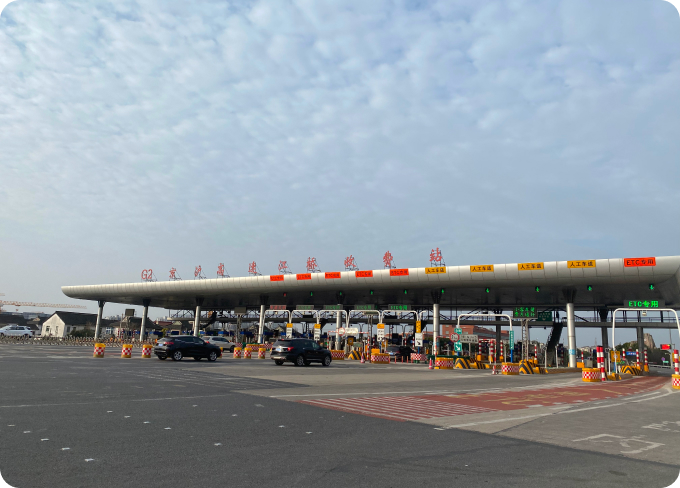
 G2 Jing-Hu Expressway (Shanghai Section) Jiangqiao Toll Staton
G2 Jing-Hu Expressway (Shanghai Section) Jiangqiao Toll Staton -
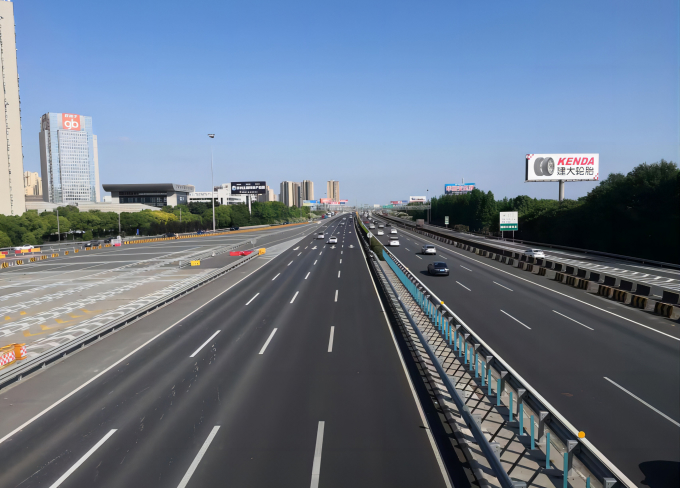
 G2 Jing-Hu Expressway (Shanghai Section) Mainline
G2 Jing-Hu Expressway (Shanghai Section) Mainline
-
-
G60 Hu-Kun Expressway (Shanghai Section)
The G60 Hu-Kun Expressway (Shanghai Section) stretches for 47.67 kilometers, beginning in Xinzhuang Town in Minhang District and extending west to Fengjing Town in Jinshan District. This section crosses three administrative regions and connects with the Hangzhou-Ningbo Expressway in Zhejiang Province. It serves as a transportation hub in the southwest of Shanghai and is a vital component of the national highway network.
-
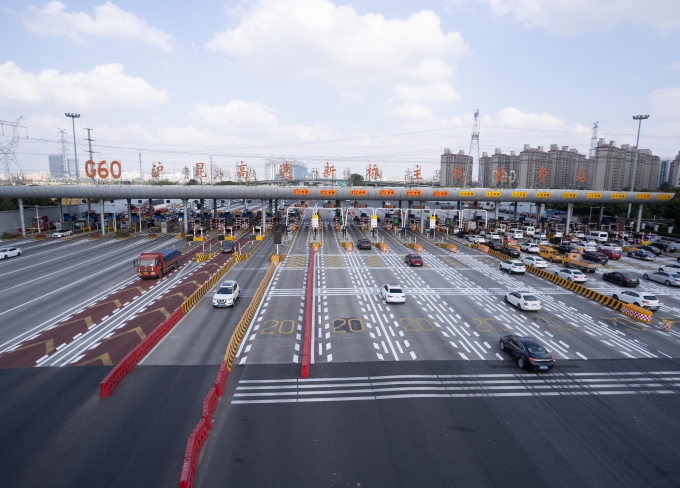
 G60 Hu-Kun Expressway (Shanghai Section) Xinqiao Mainline Toll Station
G60 Hu-Kun Expressway (Shanghai Section) Xinqiao Mainline Toll Station -
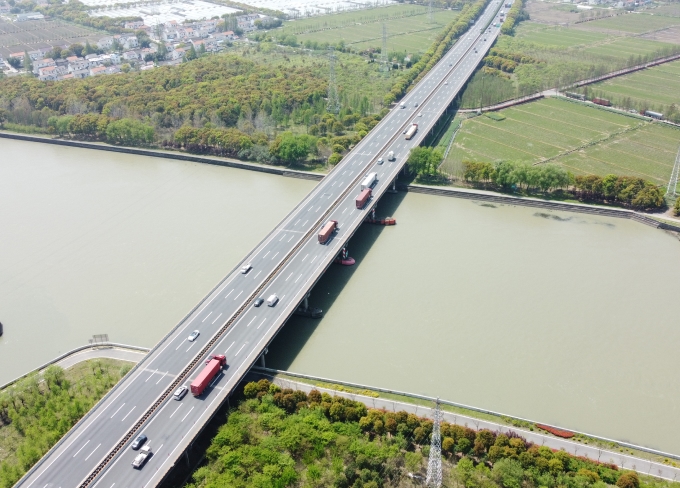
 G60 Hu-Kun Expressway (Shanghai Section) Mainline
G60 Hu-Kun Expressway (Shanghai Section) Mainline
-
-
G50 Hu-Yu Expressway (Shanghai Section)
The G50 Hu-Yu Expressway (Shanghai Section) runs for 47.2 kilometers, connecting to Yan'an Elevated Road, which traverses the heart of Shanghai. It begins at Outer Ring Road in the east and ends in Jinze Town. This expressway provides the quickest access in and out of downtown Shanghai from the western suburbs and serves as a major roadway connecting Shanghai to the hinterlands of the Yangtze River Delta and western China.
-
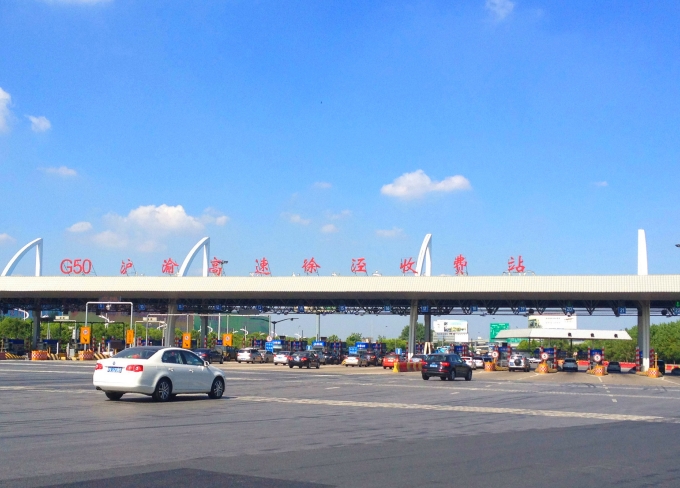
 G50 Hu-Yu Expressway (Shanghai Section) Xujing Toll Station
G50 Hu-Yu Expressway (Shanghai Section) Xujing Toll Station -
 G50 Hu-Yu Expressway (Shanghai Section) Mainline
G50 Hu-Yu Expressway (Shanghai Section) Mainline
-
-
Hangzhou Bay Bridge
The Hangzhou Bay Bridge runs from Zhengjiadai in Haiyan, Jiaxing , Zhejiang Province in the north, and ends at Shuiluwan in Cixi , Ningbo in the south. With a total length of 36 kilometers, it is designed to accommodate six lanes in both directions, allowing for speeds of up to 100 kilometers per hour and a service life of 100 years. This bridge shortens the land route between Ningbo and Shanghai by 120 kilometers and represents a significant transportation infrastructure project designed, constructed, managed, and funded entirely by China.
-
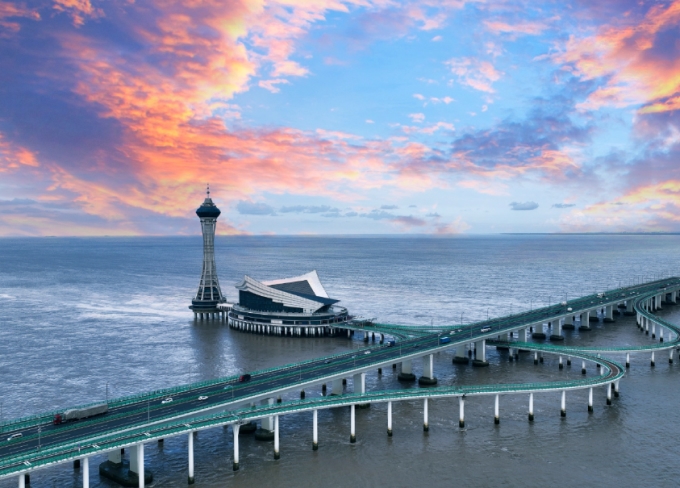
 Hangzhou Bay Bridge
Hangzhou Bay Bridge -
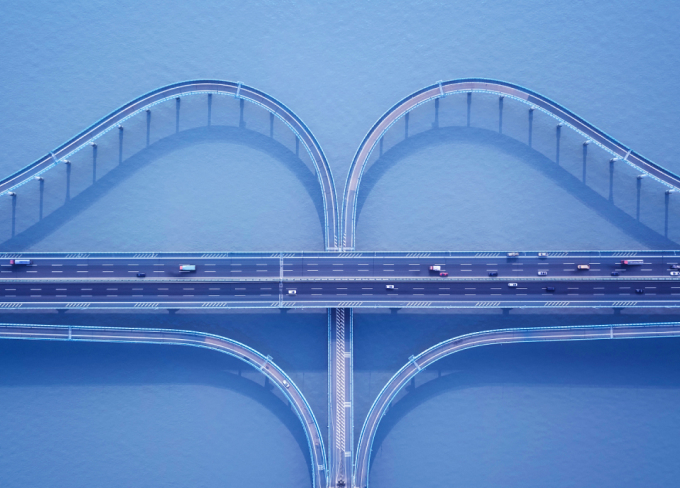
 Hangzhou Bay Bridge
Hangzhou Bay Bridge
-
-
General Water of China Co., Ltd.
Founded in November 2003 through a partnership between China Energy Conservation and Environmental Protection Group (CECEP) and Shanghai Industrial Holdings Limited (SIHL), General Water of China Co., Ltd. has a registered capital of CNY2.33334 billion. As of the end of 2023, the company manages 34 water treatment plants and 27 sewage treatment works, with a total capacity of 6.53 million tons per day and a pipeline network measuring 6,248 kilometers in length.
As a comprehensive service provider in the water sector, General Water of China offers various services, including water consulting, technical solutions, project investment, engineering construction, and operations, to governments and industrial groups. Its business scope covers water sourcing, raw water supply, potable water, sewage treatment, reclaimed water, and the harmless disposal of sludge.
Since its inception, the company has been recognized as one of the "Top 10 Influential Enterprises in the Water Industry" in China for 21 years in a row, maintaining a third-place position for the past six years. It has also been featured six times in the "Top 50 Chinese Environmental Companies." Since 2009, it has earned the title of "Flagship Water Enterprise" from the Ministry of Water Resources of the People's Republic of China for many years running. In 2010, it received the "2010 Excellence in Growth Award" from the established growth-focused consulting firm Frost & Sullivan, and was listed among the "China's Low-Carbon Environment Top 100 Enterprise Promotion, China's Sustainable Development." In 2015, the company was honored with the "Best Responsible Brand Award" at the China Charity Festival, recognized as the most influential event in Chinese philanthropy.
-
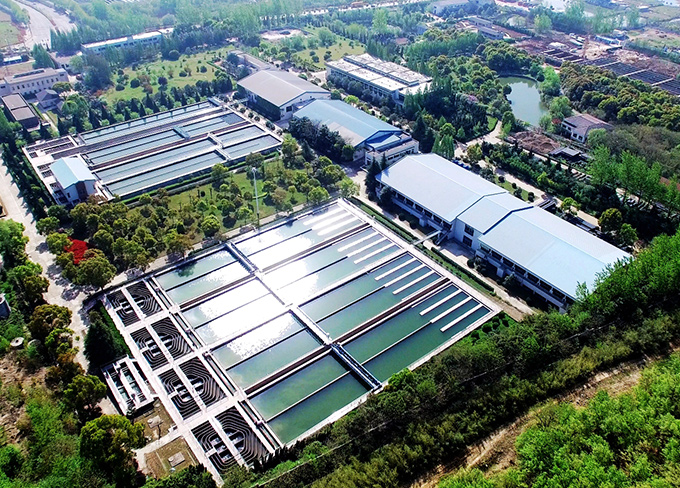
 Heihushan Water supply plant of GECGW Bengbu Co., Ltd
Heihushan Water supply plant of GECGW Bengbu Co., Ltd -
 GECGW Huaiyuan Co., Ltd
GECGW Huaiyuan Co., Ltd -
 Huzhou Laohutan Reservoir
Huzhou Laohutan Reservoir -
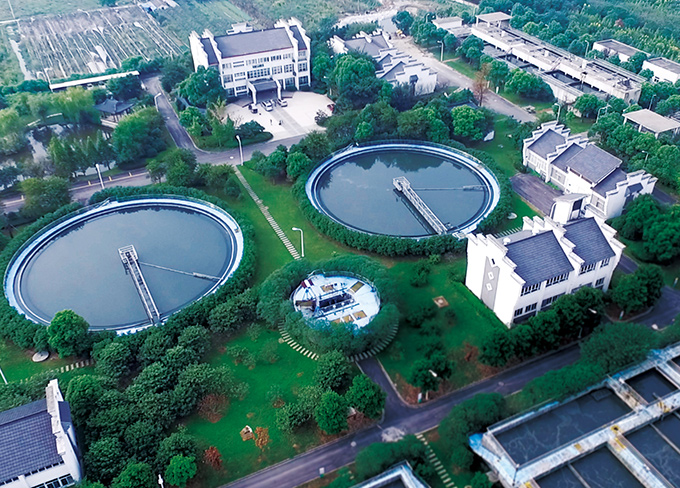
 Huzhou Eastern Area Sewage Treatment Plant
Huzhou Eastern Area Sewage Treatment Plant -
 Wastewater Treatment Project for the Supporting Park of the Environmental Comprehensive Improvement of the Children's Clothing Industrial Park in Wuxing, Huzhou
Wastewater Treatment Project for the Supporting Park of the Environmental Comprehensive Improvement of the Children's Clothing Industrial Park in Wuxing, Huzhou -
 Xiangtan No.3 water purification plant
Xiangtan No.3 water purification plant -
 Xiangtan Hedong Sewage Treatment Plant
Xiangtan Hedong Sewage Treatment Plant -
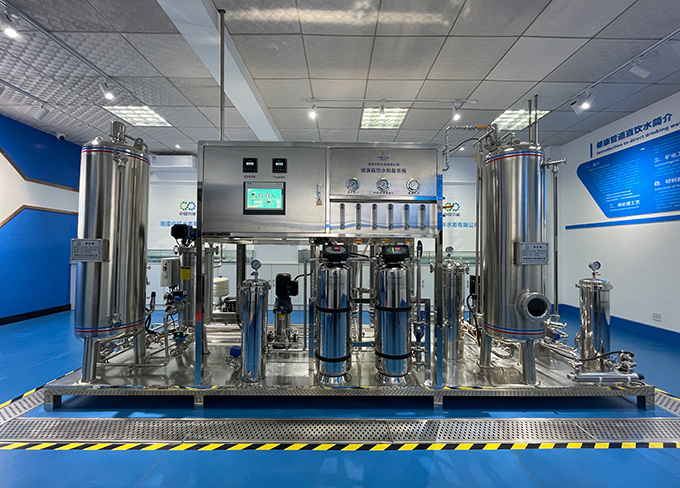
 Equipment process diagram of the demonstration project for piped direct drinking water in Tanshui Building
Equipment process diagram of the demonstration project for piped direct drinking water in Tanshui Building -
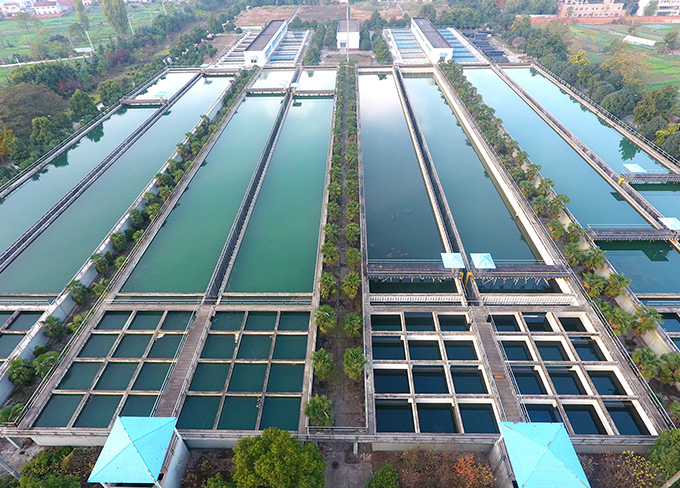
 Aerial photography of GECGW Xiangyang Co., Ltd
Aerial photography of GECGW Xiangyang Co., Ltd
-
-
Canvest Environmental Protection Group Company Limited
Canvest Environmental Protection Group Company Limited ("Canvest") is a leading provider of urban comprehensive environmental and sanitation services, as well as smart city management solutions. Since 2003, the company has focused on the "Waste-to-Energy" industry, initially starting with generating electricity through waste incineration. It has adopted an "Incineration Plus" business strategy, extending its operations both upstream and downstream within the industry chain. Canvest actively develops sanitation services, landfill remediation, and steam supply collaboration, while delivering high-quality services for smart city management. In 2014, it was listed on the main board of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange under the stock code 01381. As of the end of 2023, SIIC owned a 19.48% share in Canvest.
With two decades of robust management and high-quality development, Canvest has evolved into a diversified modern enterprise group. Its operations span various areas including generating electricity through domestic waste incineration, kitchen waste treatment, general industrial and hazardous waste treatment, landfill management, legacy waste processing, urban cleaning services, integrated sanitation operation and management, and comprehensive smart city management, forming a strong collaborative development framework across the entire industry chain.
By the end of 2023, Canvest had 36 projects of generating electricity through waste incineration, spanning 12 provinces and 26 cities, with a waste processing capacity of 54,540 tons per day.
-
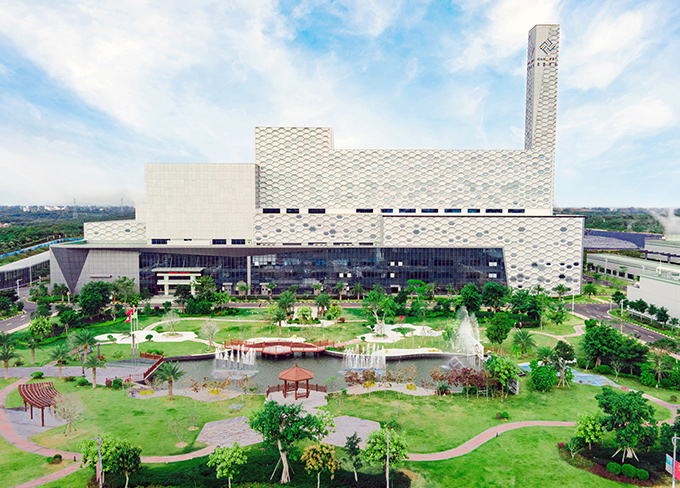
 Canvest Dianbai Waste-to-energy project
Canvest Dianbai Waste-to-energy project -
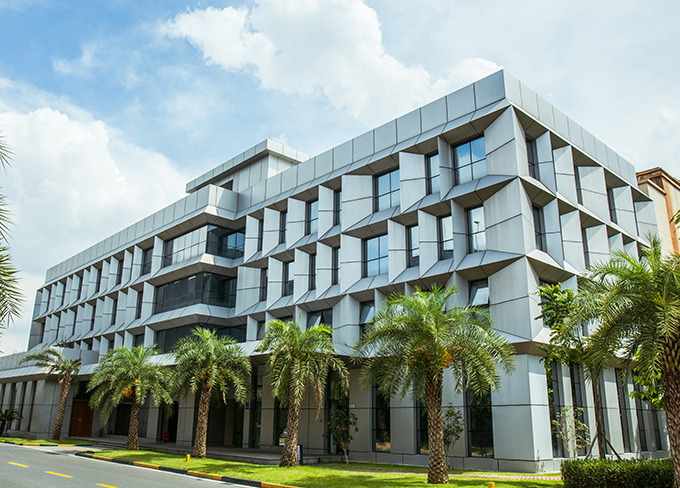
 Canvest Hengli Waste-to-energy projects
Canvest Hengli Waste-to-energy projects -
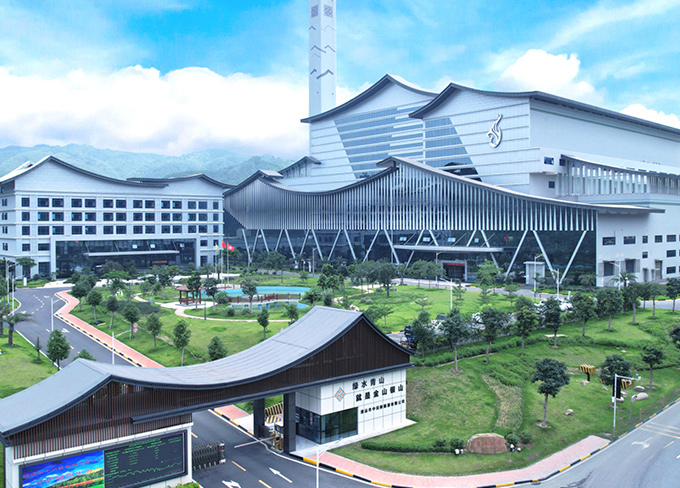
 Canvest Qingyuan Waste-to-energy project
Canvest Qingyuan Waste-to-energy project -
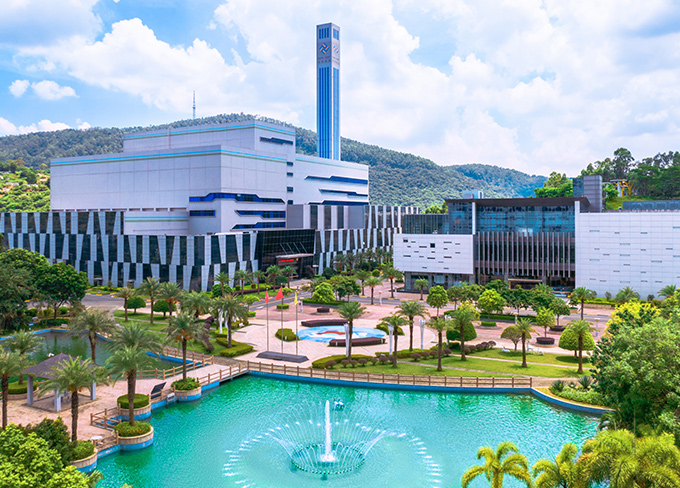
 China Scivest II Waste-to-energy project
China Scivest II Waste-to-energy project -
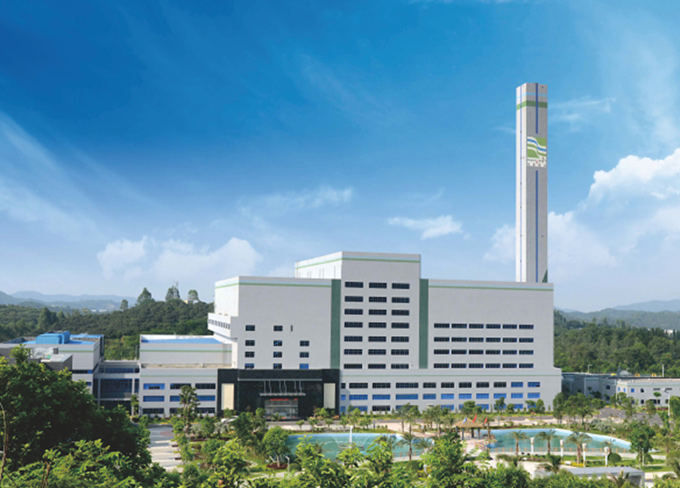
 China Scivest I Waste-to-energy project
China Scivest I Waste-to-energy project -
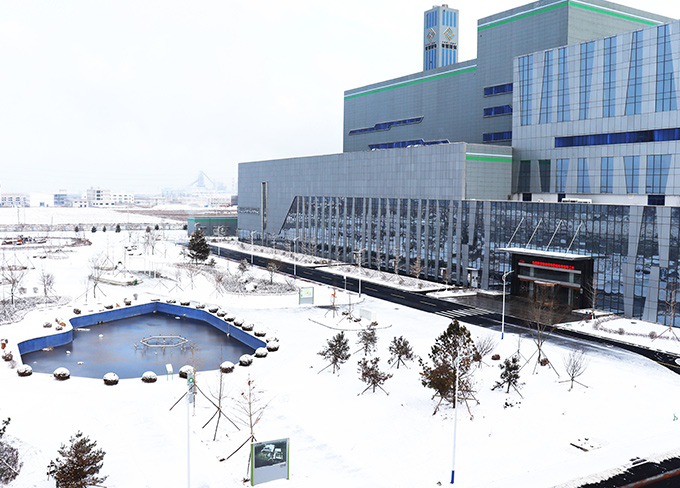
 Canvest Yingkou Waste-to-energy project
Canvest Yingkou Waste-to-energy project
-
-
Shanghai SUS Environment Co., Ltd.
Shanghai SUS Environment Co., Ltd. ("SUS Environment") is a leading global provider of integrated environmental services across the full industry chain. The company's main activities are centered on the investment, construction, operation, and technological transformation of waste-to-energy projects. Additionally, SUS Environment engages in the investment, construction, and operation of low-carbon eco-industrial parks (EIP), supplies incineration equipment and critical technologies, offers comprehensive energy utilization, manages sludge treatment and disposal, performs environmental restoration, and provides low-carbon solutions. As of now, SIIC possesses a 28.34% equity interest in SUS Environment.
As of June 2024, the company has invested in and constructed a total of 84 waste-to-energy projects worldwide, with a daily capacity for handling 110,000 tons of household waste. The company has been awarded the title of "Top 10 Influential Enterprises in Solid Waste" for seven consecutive years.
SUS Environment is identified as a specialized and sophisticated "little giant" enterprise that produces new and unique products by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. The company has developed its own waste incineration equipment and key technologies, which have received a number of accolades, including the second prize for National Science and Technology Progress Award, the first prize for Science and Technology Progress Award from the Ministry of Education, the first prize for Huaxia Construction Science and Technology Award, and the first prize for Science and Technology Progress Award from the China Association of Circular Economy. Leveraging these achievements, SUS Environment has developed a series of highly effective, low-carbon, ultra-clean, and intelligent solid waste disposal technologies, consistently raising the overall standards of the industry and advancing China's solid waste disposal technology to an internationally leading position.
Moving forward, SUS Environment will stay committed to its mission of "creating a cleaner and more friendlier living environment." It will embrace the values of "integrity, responsibility; teamwork, innovation; customer, coalition." By focusing on comprehensive management approaches that prioritize reduction, resource recovery, and harmless processing, the company seeks to achieve sustainable development goals for both people and the environment.
-
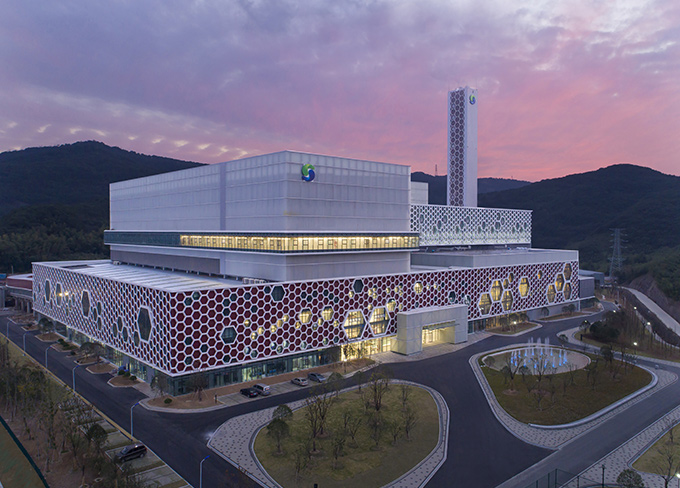
 Most Beautiful Waste-to-Energy Plant in China, Ningbo Project
Most Beautiful Waste-to-Energy Plant in China, Ningbo Project -
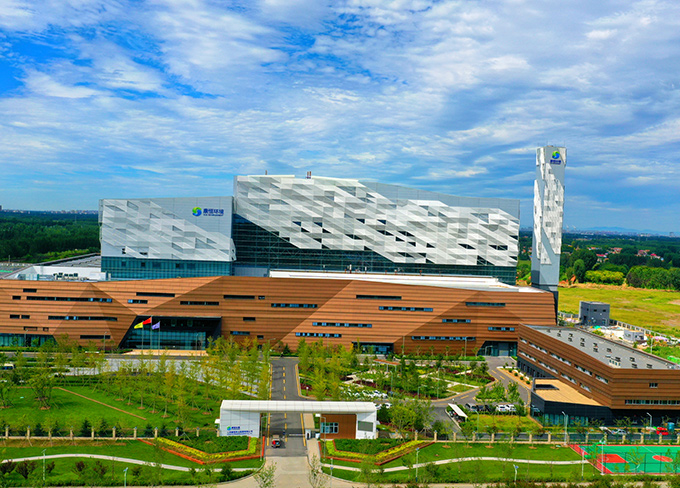
 First homemade thousand-ton Grate in China, Sanhe Project
First homemade thousand-ton Grate in China, Sanhe Project -
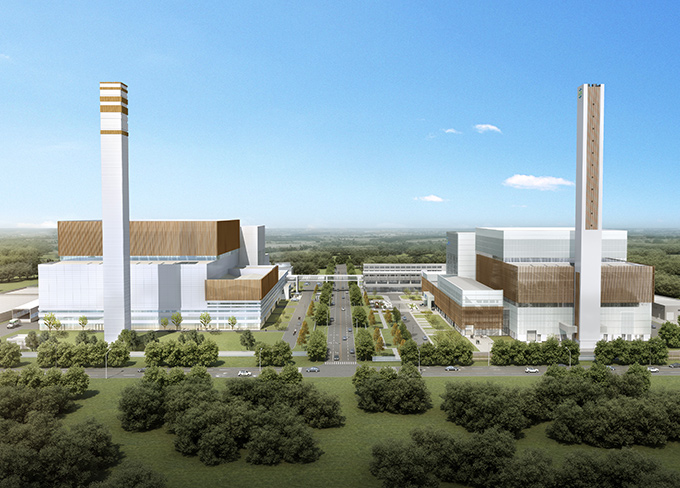
 National AAA Level Waste-to-Energy Project, Zhuhai Project Phase I and Phase II
National AAA Level Waste-to-Energy Project, Zhuhai Project Phase I and Phase II -

 China Construction Engineering Luban Prize, Qingdao West Coast Project
China Construction Engineering Luban Prize, Qingdao West Coast Project -
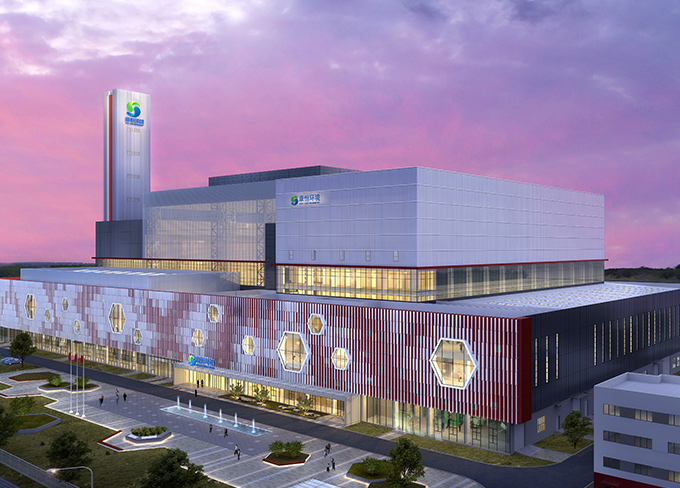
 Ecology and Environment Education Base of Ministry of Ecology and Environment, Xian Gaoling Project
Ecology and Environment Education Base of Ministry of Ecology and Environment, Xian Gaoling Project -
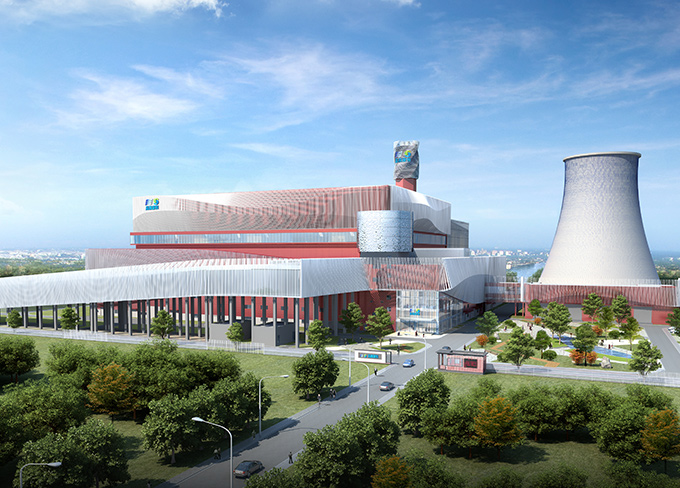
 First Fluidized Bed Transformation Engineering in China, Jiaxing Project
First Fluidized Bed Transformation Engineering in China, Jiaxing Project -
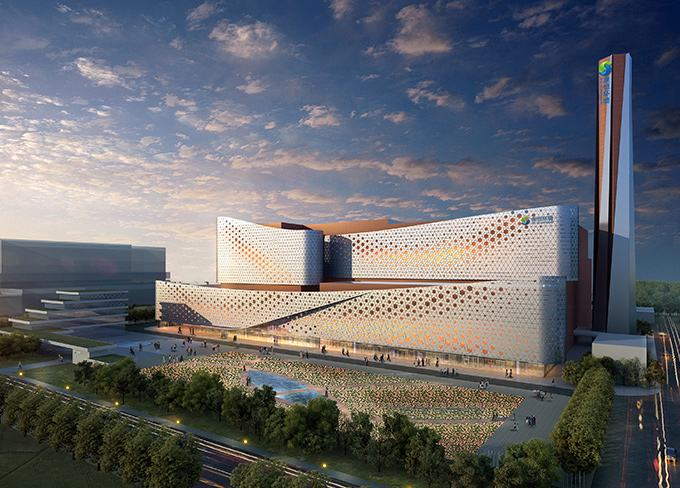
 PPP Demonstrative Project of Ministry of Finance, Qingdao Xiaojianxi Project
PPP Demonstrative Project of Ministry of Finance, Qingdao Xiaojianxi Project -
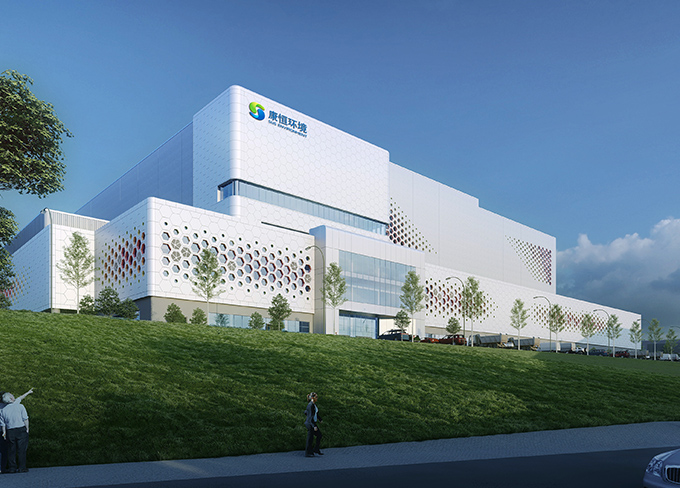
 Paris DNA Design Award of the French Republic — Liuzhou Project
Paris DNA Design Award of the French Republic — Liuzhou Project -
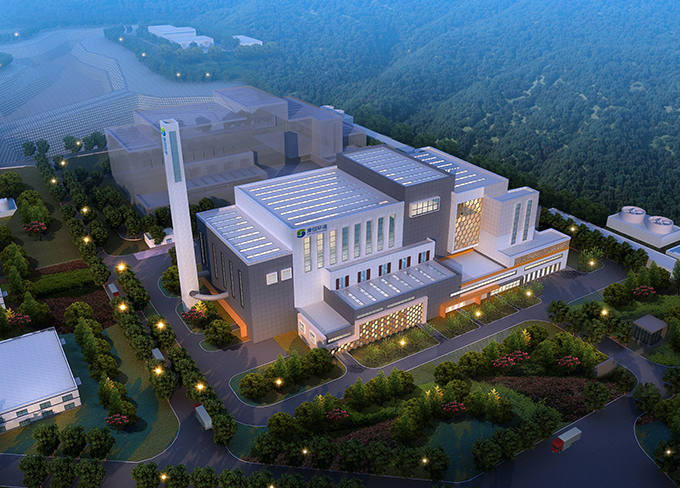
 PPP Demonstration Project of the National Development and Reform Commission & Ministry of Finance — Wuzhou Project
PPP Demonstration Project of the National Development and Reform Commission & Ministry of Finance — Wuzhou Project
-





